[コンプリート!] greenhouse effect greenhouse gas emissions diagram 349457
Greenhouse Effect Contents Atmosphere Key Terms Gases Causes Effects Atmosphere Exosphere Thermosphere Mesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere Troposphere Lowest portion of earth's atmosphere 75% of the entire atmosphere mass Water Vapor Aerosols 0 km – 10 km Depth ~ 10 km Warmer nearest earth Colder the further you go Travel Back to the Atmosphere StratosphereOceanographer Josh Willis discusses the heat capacity of water, performs an experiment to demonstrate heat capacity using a water balloon and describes how water's ability to store heat affects Earth's climate Video Oceans of Climate Change Carbon dioxide is the main heattrapping greenhouse gas that humans emit This article tries to answer a question about the greenhouse effect "Greenhouse gases prevent the infrared rays from leaving the Earth's atmosphere, but why do they not prevent additional solar radiation from entering the atmosphere?" The key is the different wavelength (or different frequency) of solar light and infrared light Let's have a look at the greenhouse effect

What S Going On In This Graph Nov 19 The New York Times
Greenhouse effect greenhouse gas emissions diagram
Greenhouse effect greenhouse gas emissions diagram-How the greenhouse effect works It's thought that the buildup of greenhouse gases impacts on global temperature in two ways The gases allow more of the sun's rays to enter the atmosphereAs a result, average surface temperatures are rising




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research
How do greenhouse gases affect the climate?This chart maps out future greenhouse gas emissions scenarios under a range of assumptions if no climate policies were implemented;The impacts of an eruption on the greenhouse effect During a volcanic eruption, the main greenhouse gas that is emitted is carbon dioxide During an eruption, huge amounts of CO₂may be released (approximately 026 Gt/y globally 3 ), leading to an overall heating of the earth and its atmosphere through an accelerated greenhouse effect
New Zealand's greenhouse gas emissions is a direct measure of the 'Human activities generating greenhouse gases' topic Stats NZ and the Ministry for the Environment must report on topics related to the five environmental domains air, atmosphere and climate, fresh water, land, and marine These topics identify key issues within each domainThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it Similarly, aerosols have radiatively active effectsCarbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, nitrous oxide and lowlevel ozone See greenhouse effect Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 08 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
And necessary pathways which are compatible with limiting warming to 15°C or 2°C of warming this century 14Explore the atmosphere during the ice age and today What happens when you add clouds?The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, but the extra gases produced by human activity are making it stronger We are now adding to these gases faster than oceans and plants can absorb them — the greenhouse effect is being 'enhanced' by humans




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov



Earthcharts Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector
If all countries achieved their current future pledges for emissions reductions; Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere that produce the greenhouse effect Changes in the concentration of certain greenhouse gases, from human activity (such as burning fossil fuels), increase the risk of global climate change Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, nitrous oxide, halogenatedForm definitions of the greenhouse effect based on prior knowledge, class discussion, and viewing diagrams 2 Participate in group brainstorming sessions and class discussions related to the impact of the greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Analyze global warming diagrams and resources to obtain a clear understanding of this scientific




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering
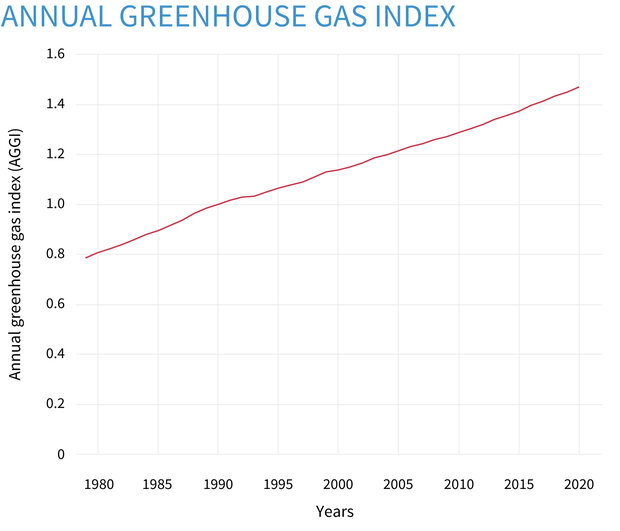



Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
Carbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas you hear people talk about the most That's because we produce more carbon dioxide than any other greenhouse gas, and it's responsible for most of the warming Some greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere for only a short time, but others can stay in the atmosphere and affect the climate for thousands of yearsThe amount of greenhouse gases increases the planet's surface temperature by increasing the amount of heat that is trapped in the lowest part of the atmosphere What is controversial about the greenhouse effect is exactly how much Earth's surface temperature will rise given a certain increase in a trace greenhouse gas such as CO2Greenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by about 80 percent during that time The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today far




U S Ghg Emissions Flow Chart Visual Ly Greenhouse Gases Ghg Emissions Climate Change




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does notChange the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes Then compare to the effect of glass panes Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?




Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From University Of California
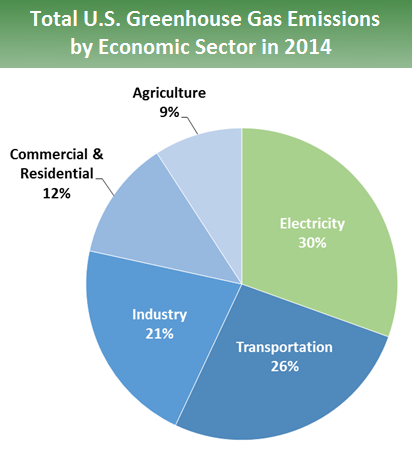



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
If current policies continued;This warms Earth's atmosphere, making our planet habitable; WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin The World Meteorological Organization's Greenhouse Gas Bulletin is published annually to report on the latest trends in atmospheric concentrations of the most important longlived greenhouse gases carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) climate change, carbon dioxide, greenhouse



Chart China Beats U S Europe In Combined Greenhouse Gases Statista



Greenhouse Gases Transportation Benefit Cost Analysis
The other 80% of GHG emissions from natural gas result from gas combustion by enduse consumers The Sankey diagrams in this paperA gas that absorbs heat within a planet's atmosphere, causing the greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases on earth include carbon dioxide, water vapour, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Thank you for visiting the Energy System Map If you're a young person between the age of 10, Student Energy invites you to participate in the Global Youth Greenhouse gas emissions affect more than just temperature Another effect involves changes in precipitation , such as rain and snow Over the course of the th century, precipitation increased in eastern parts of North and South America, northern Europe, and northern and central Asia



1
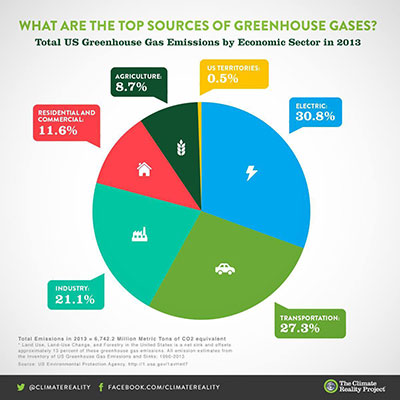



Agriculture Causes Less Emissions Than Transportation
What are the anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in the first place? Greenhouse gases have a profound effect on the energy budget of the Earth system despite making up only a fraction of all atmospheric gases Concentrations of greenhouse gases have varied substantially during Earth's history, and these variations have driven substantial climate changes at a wide range of timescales In general, greenhouse gas concentrations have beenAnd "upstream" emissions from natural gas infrastructure accounted for approximately % of total 12 greenhouse gas ( GHG) emissions from natural gas systems;
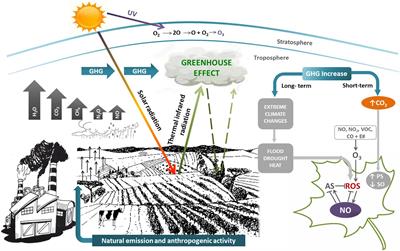



Frontiers Climate Change And The Impact Of Greenhouse Gasses Co2 And No Friends And Foes Of Plant Oxidative Stress Plant Science
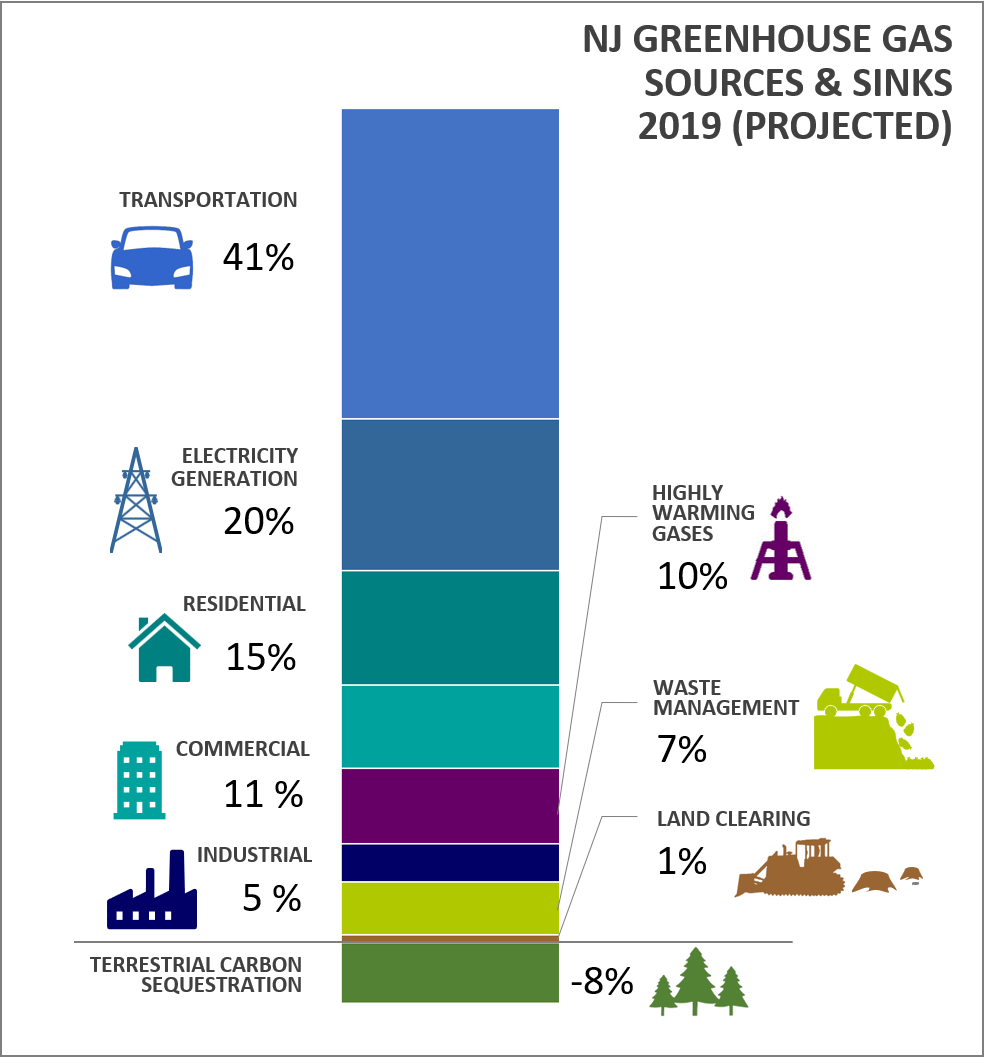



Njdep Air Quality Energy Sustainability
Carbon dioxide is an important greenhouse gas which is thought to be responsible for some fraction of the rapid increase in global warming seen especially in the temperature records in the th century, as compared with tens of thousands of years worth of temperature records which can be read from ice cores taken in Arctic regionsIndeed, the main culprit is, as we might have expected, CO 2 In terms of the net increase in the greenhouse effect due to humanproduced greenhouse gases, CO 2 is responsible for the lion's share CO 2 from fossil fuel burning alone is more than half the net forceGases in the atmosphere can contribute to the greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly Direct effects occur when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas Indirect radiative forcing occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, when a gas influences the
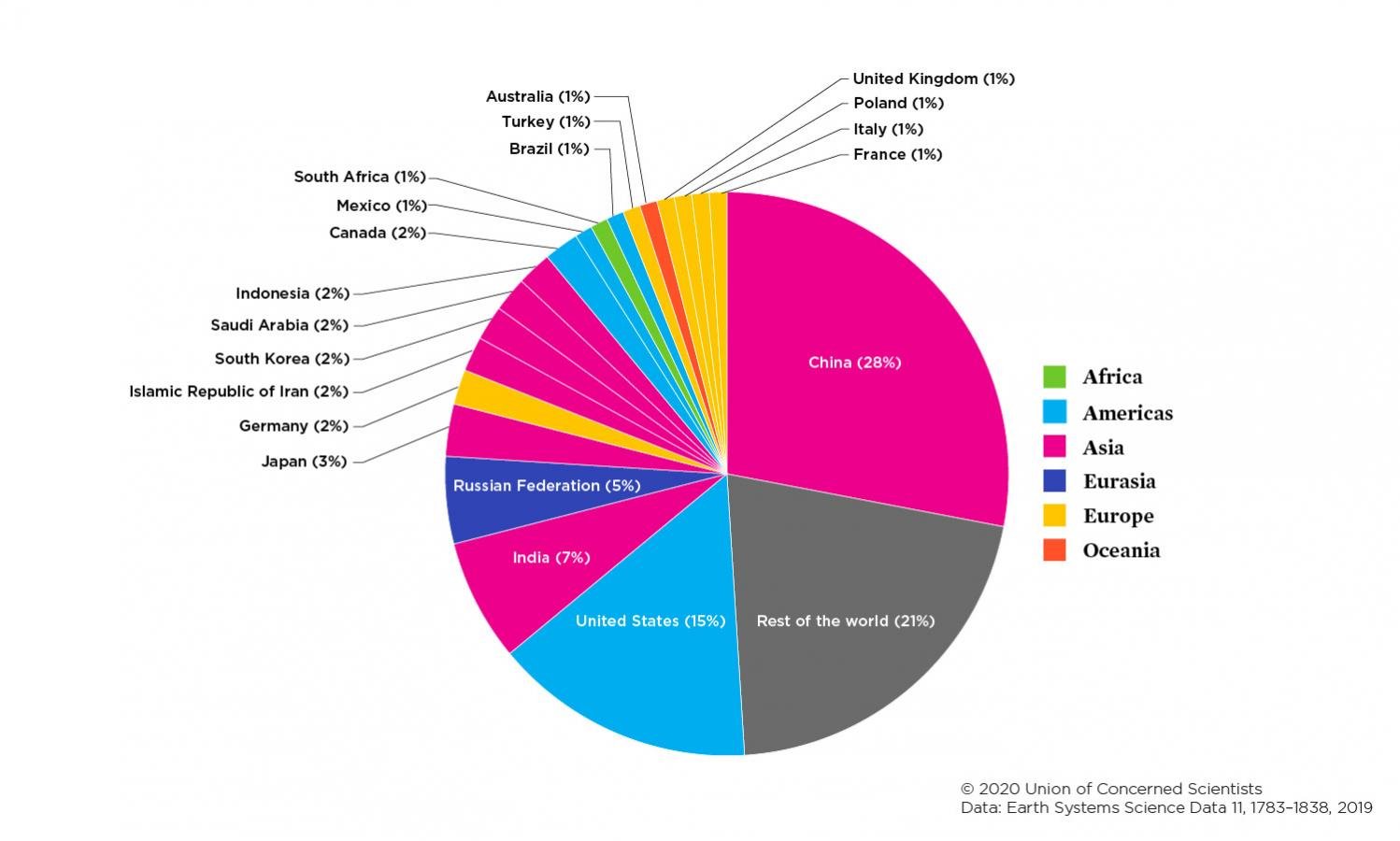



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research
Earth exists as the "just right" planet, with the greenhouse effect having just enough influence to make the planet livable Global Warming main article The rapid increase in human activities in recent history has led to the continuing emission of large amounts of greenhouse gases Although necessary in the atmosphere in smaller concentrations, the increased amount of carbon dioxide,"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozoneHuman activities have led to a build up of extra greenhouse gases in the atmsophere;
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram
'Greenhouse' gases carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, water vapour effectively prevent some of this longwave radiation from leaving the atmosphere;Greenhouse gases diagrams • Where do Greenhouse Gases Come From handouts • Greenhouse Gas Emissions Diagram handouts • Colored pencils National Science Education Standards D1h The atmosphere is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace gases that include water vapor D1j Living organisms have played many roles in the Earth system Without any greenhouse gases, Earth would be an icy wasteland Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
Greenhouse Effect A layer of gases in Earth's atmosphere naturally creates a greenhouse effect Without these gases in place, light and warmth from the sun would strike Earth, then largely The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear
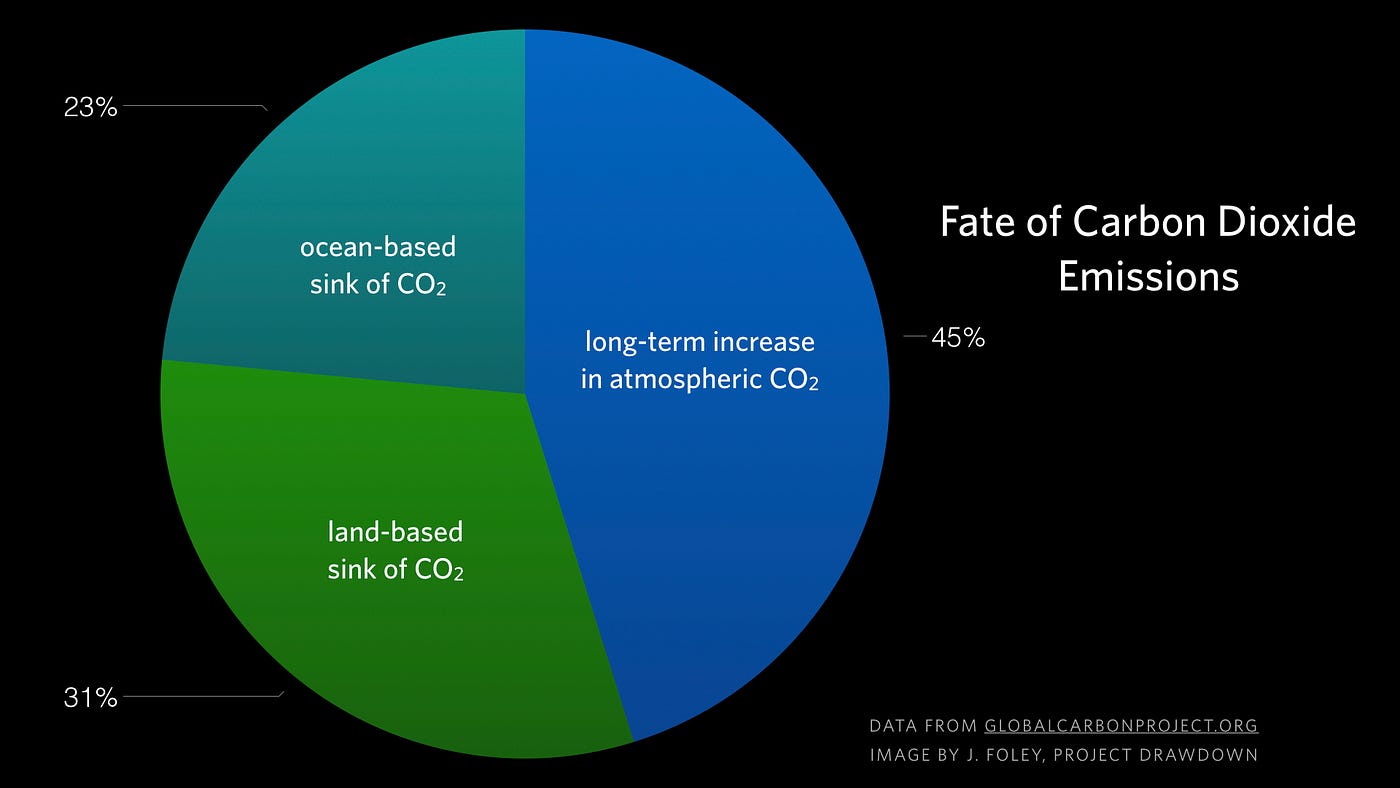



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org



Simple
The diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gas Water vapor and clouds cause most of the Earth's natural greenhouse effect and account for about 90% of the total heatretaining capacity of the atmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, trapping the heat in our atmosphere instead of letting it escape to spacePrevious reviews have quantified factors affecting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from Asian rice ( L) systems, but not from rice systems typical for the United States, which often vary considerably particularly in practices (ie, water and carbon management) that affect emissions




Windsor S Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
The increase of greenhouse gases will, theoretically, enhance the greenhouse effect by trapping more of the heat energy emitted by Earth's surface, thus increasing the surface temperatures on a global scale Scientists expect that the global average surface temperature could rise 145 F in the next 50 years and as much as 10 F in the next centuryThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to existThe earth also releases heat back toward space Some of this heat passes through the atmosphere, but most of it is captured and retained by greenhouse gases before it can escape This is the mechanism that keeps the earth warm Normally, the greenhouse effect keeps the earth just warm enough to sustain life Scientists say that without the greenhouse effect, the average
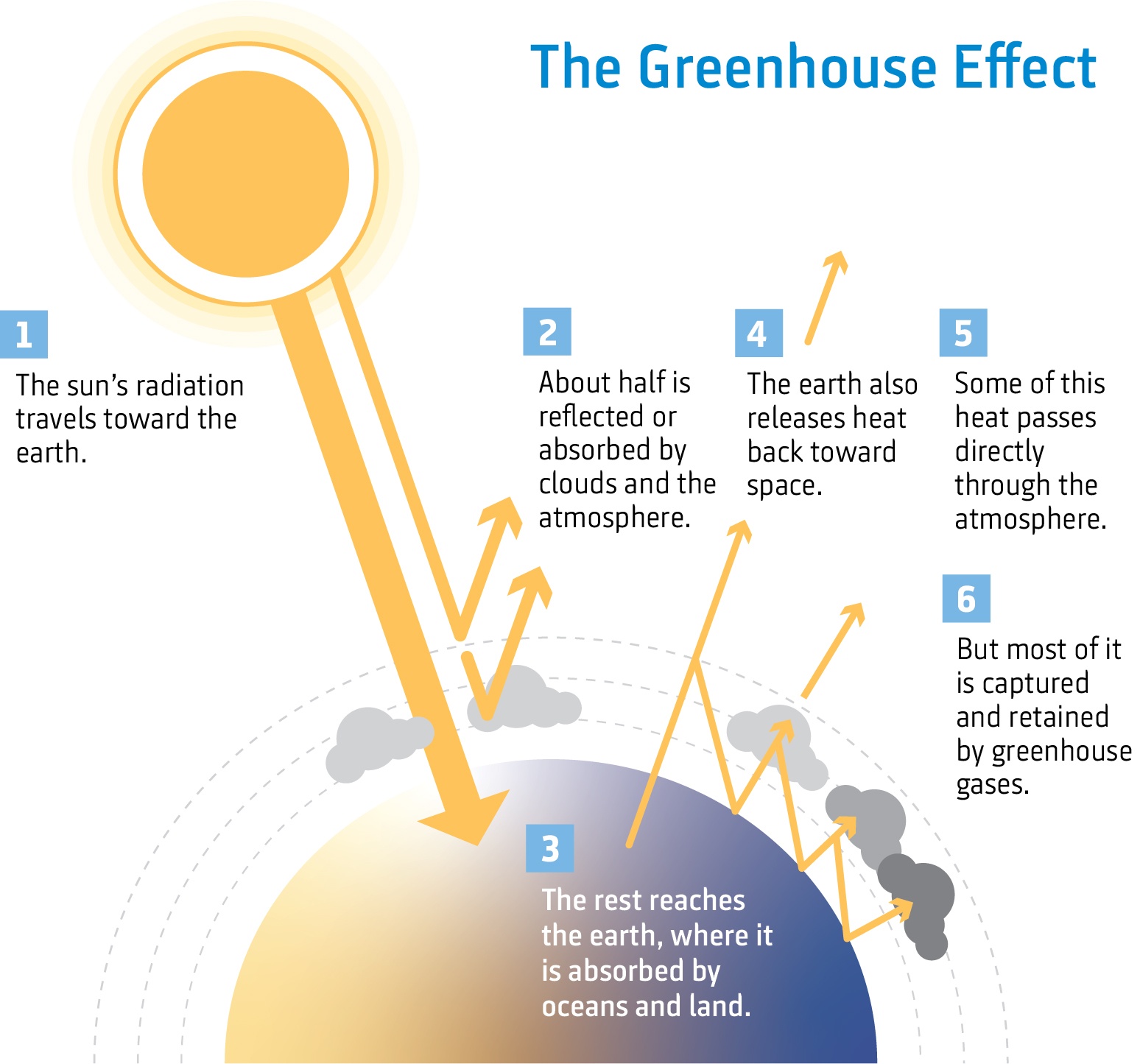



Climate Change The Science Niwa




Greenhouse Effect




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
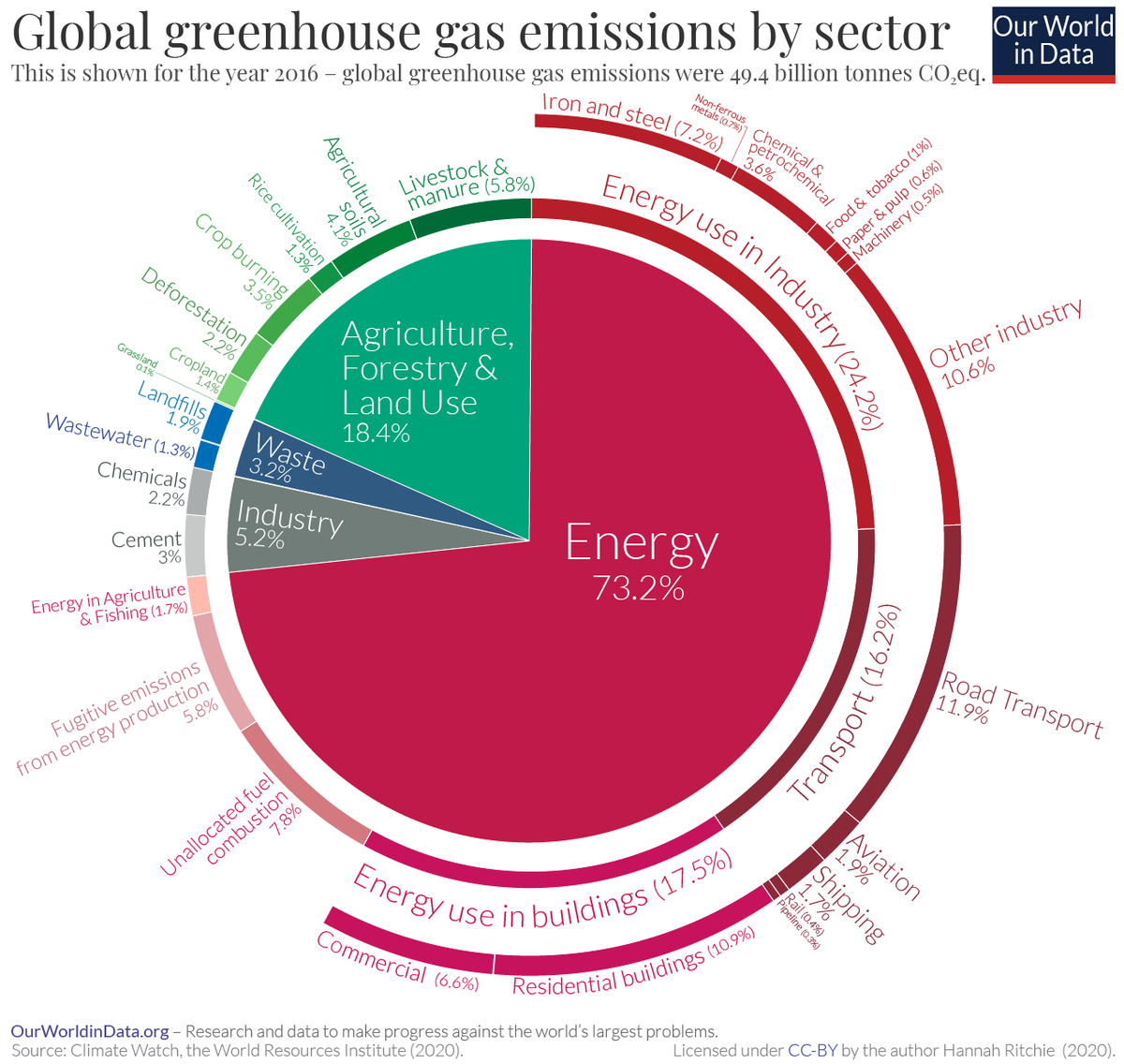



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector
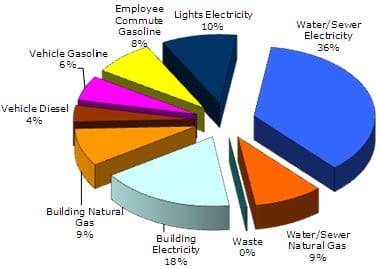



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory For Bellingham City Of Bellingham
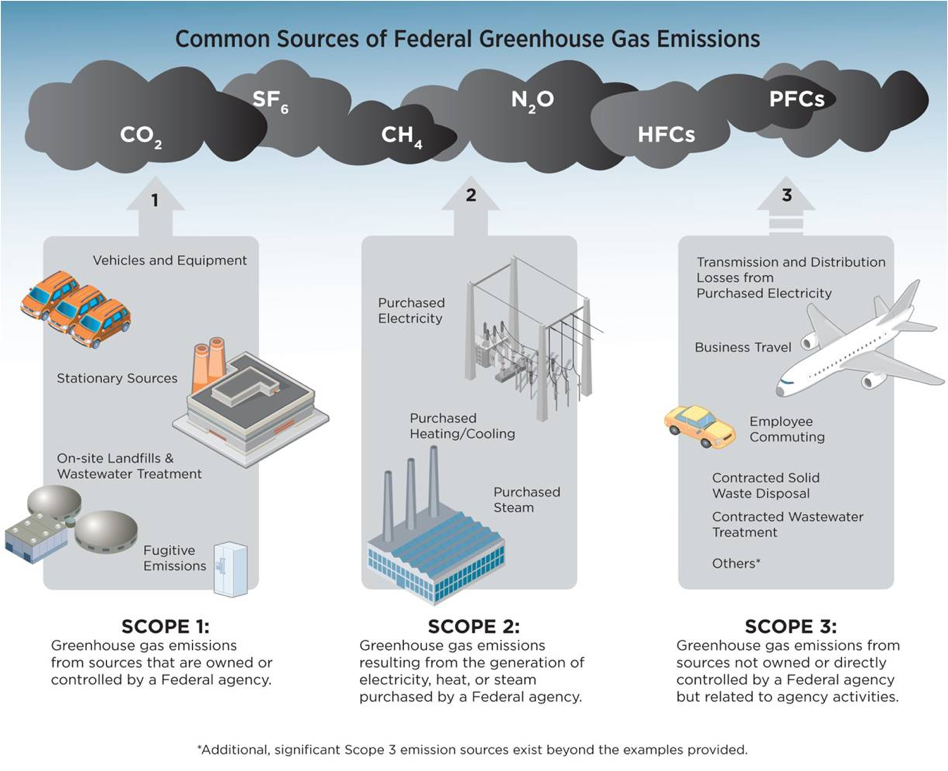



Sustainability Greenhouse Gas Reduction
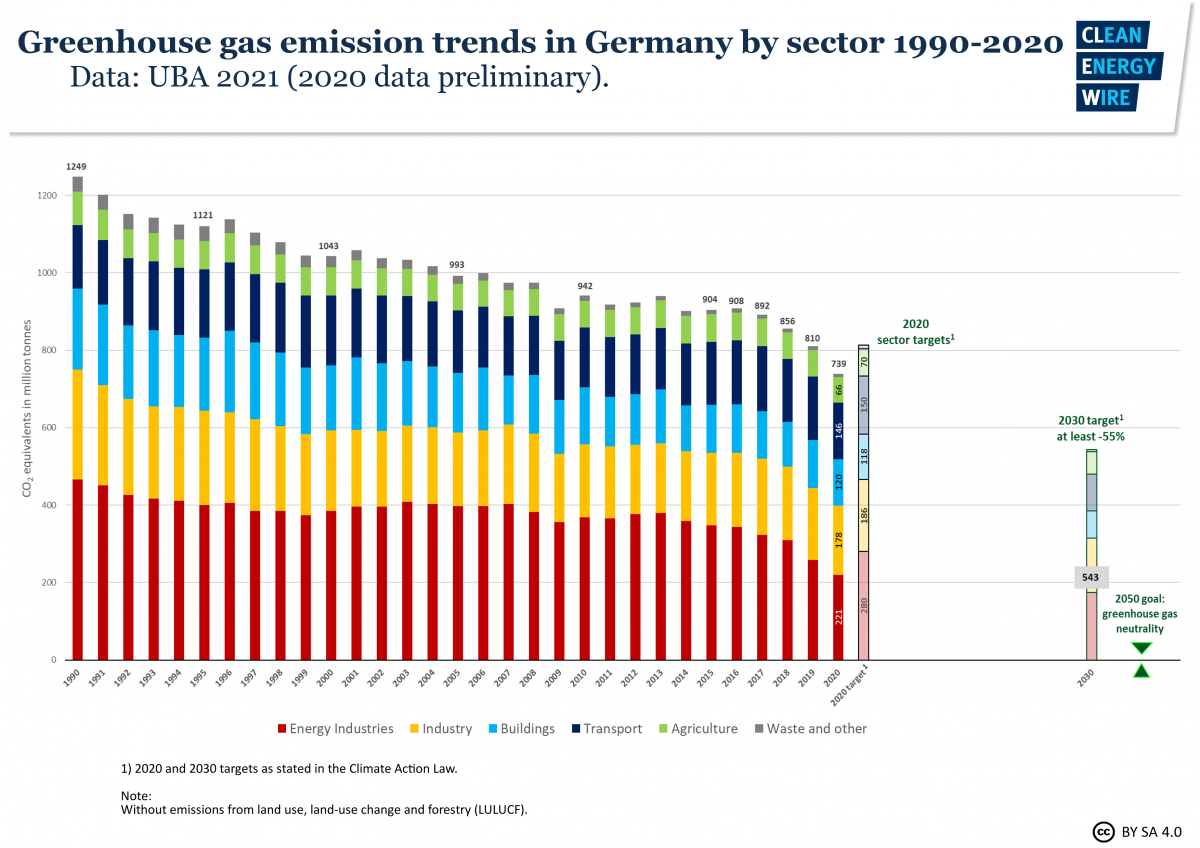



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire




The Greenhouse Effect Artis Energy




Emissions Of The Powerful Greenhouse Gas Sf6 Are Rising Rapidly World Economic Forum




The Greenhouse Effect World101




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 177 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Bikes And Walking Transit Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Source
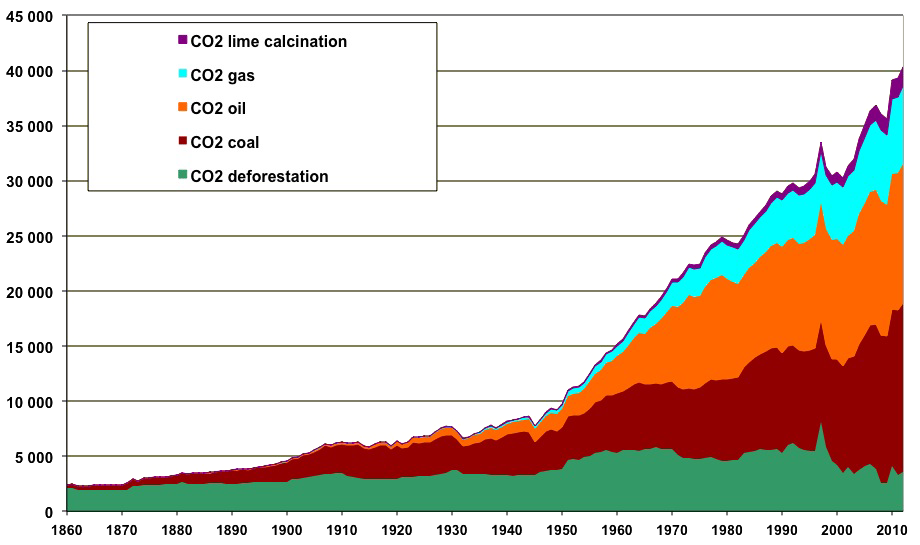



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici




What S Going On In This Graph Nov 19 The New York Times
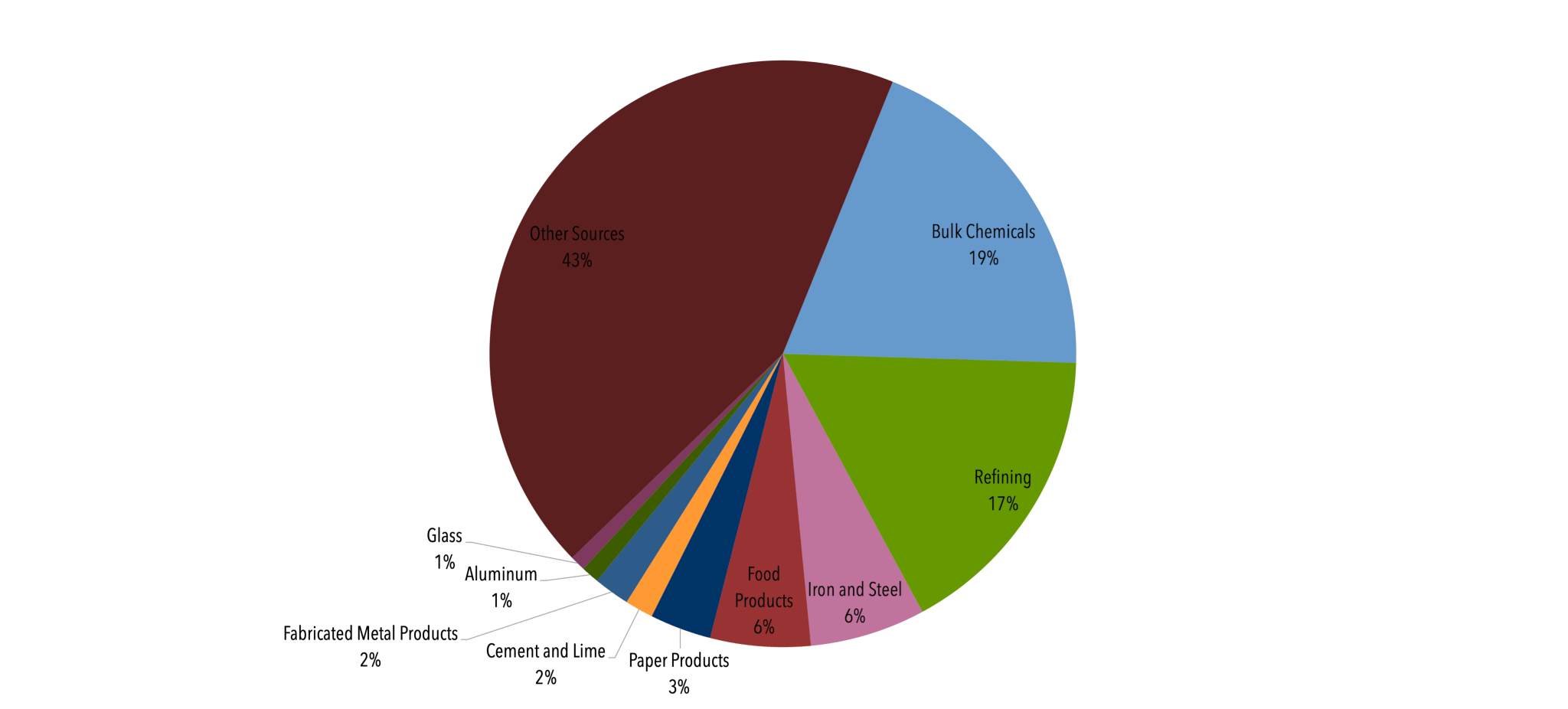



Controlling Industrial Greenhouse Gas Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Climate Greenhouse Gases Sustainability
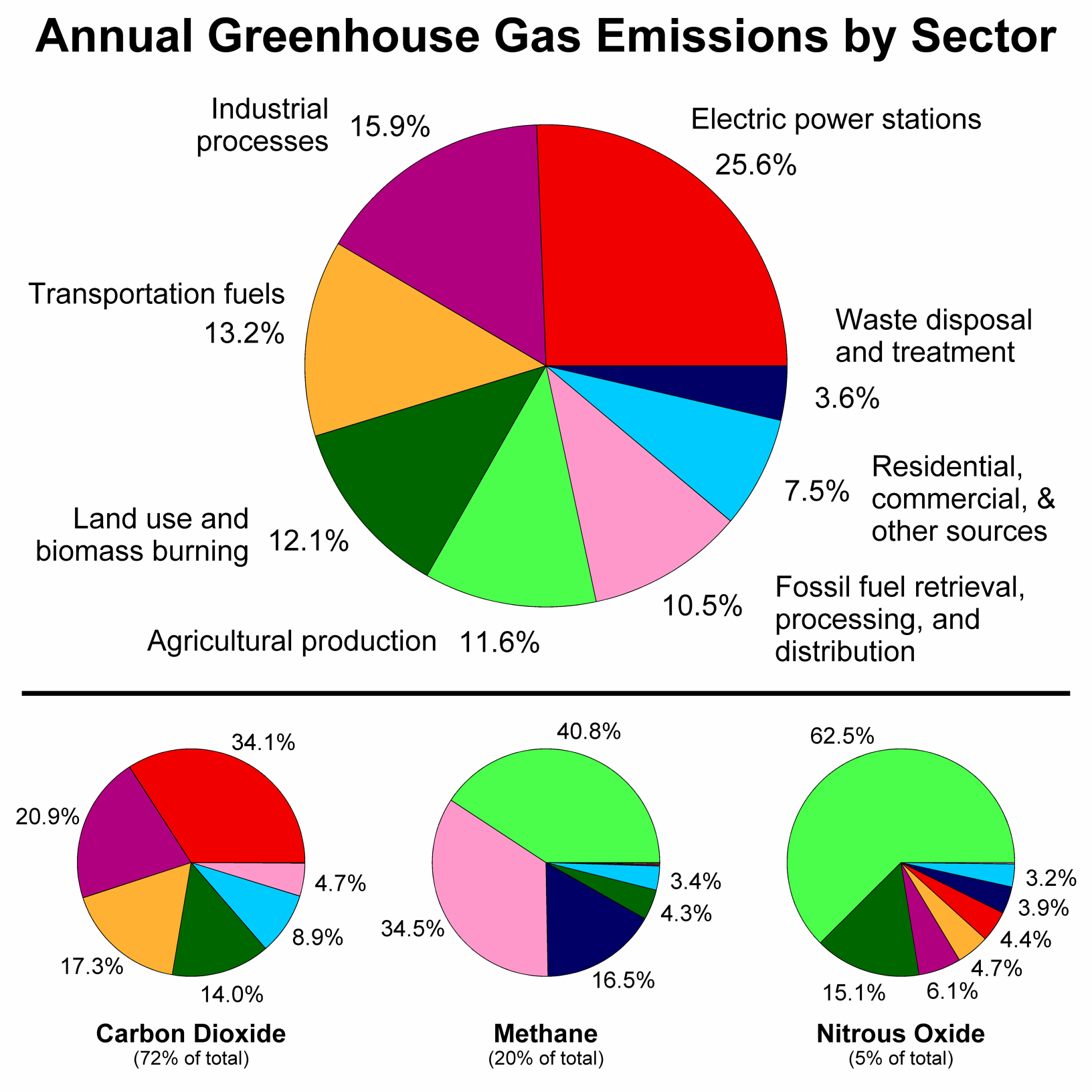



File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons



Chart Europe S Biggest Greenhouse Gas Emitters Statista
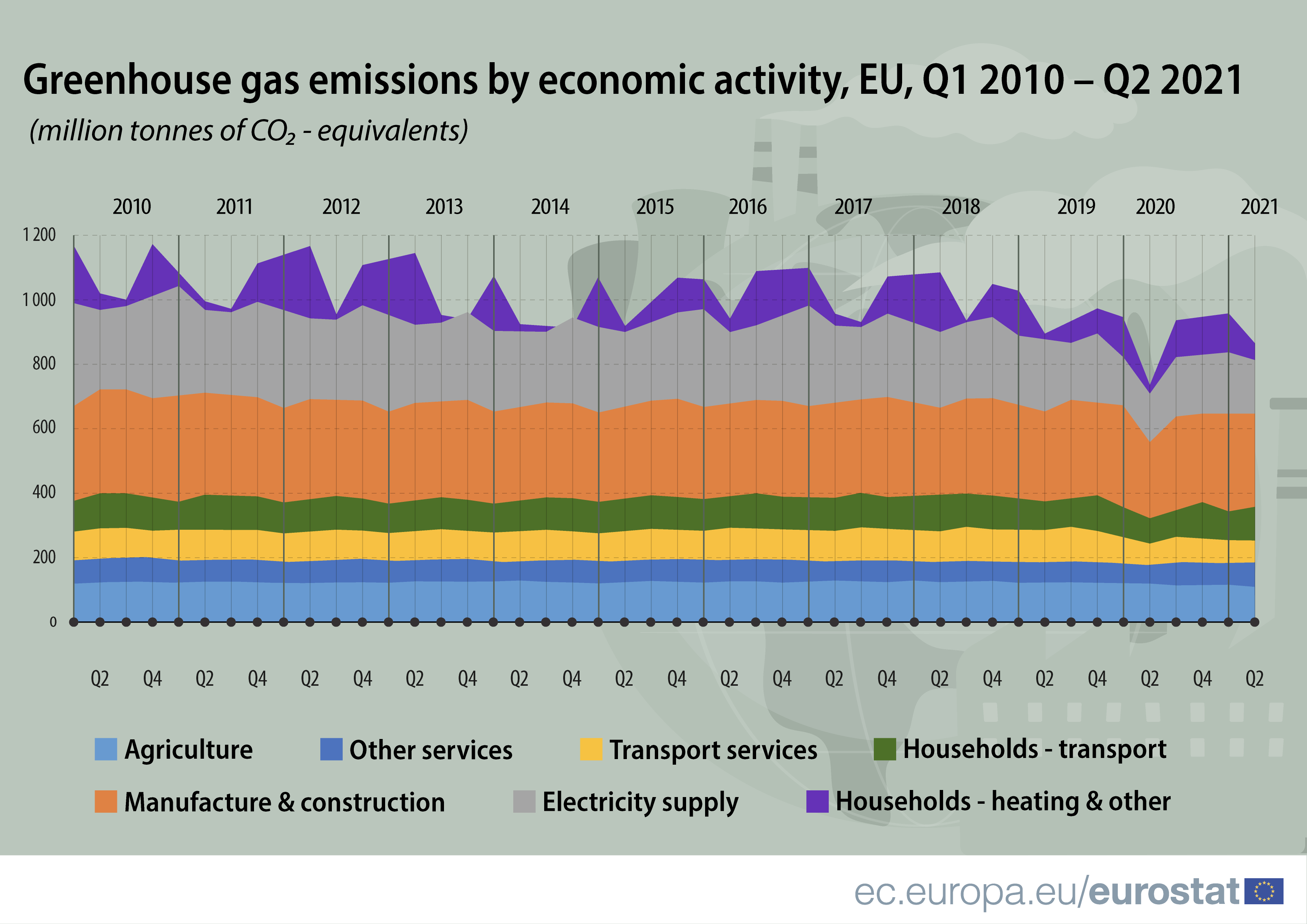



Eurostat Releases For The First Time Estimates Of Quarterly Eu Greenhouse Gas Emissions Products Eurostat News Eurostat




Emission Of Greenhouse Gases Download Scientific Diagram




Nahb Residential Greenhouse Gas Emissions
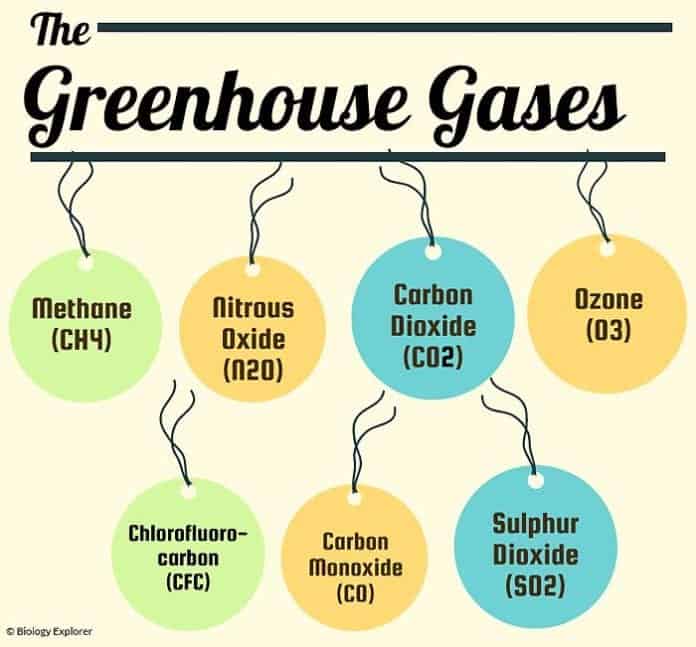



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef




Major Greenhouse Gas Reductions Needed By 50 Ipcc Climate Central




Why We Measure Track Ghgs Sustainable Practices The Office Of Sustainability Umass Lowell




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
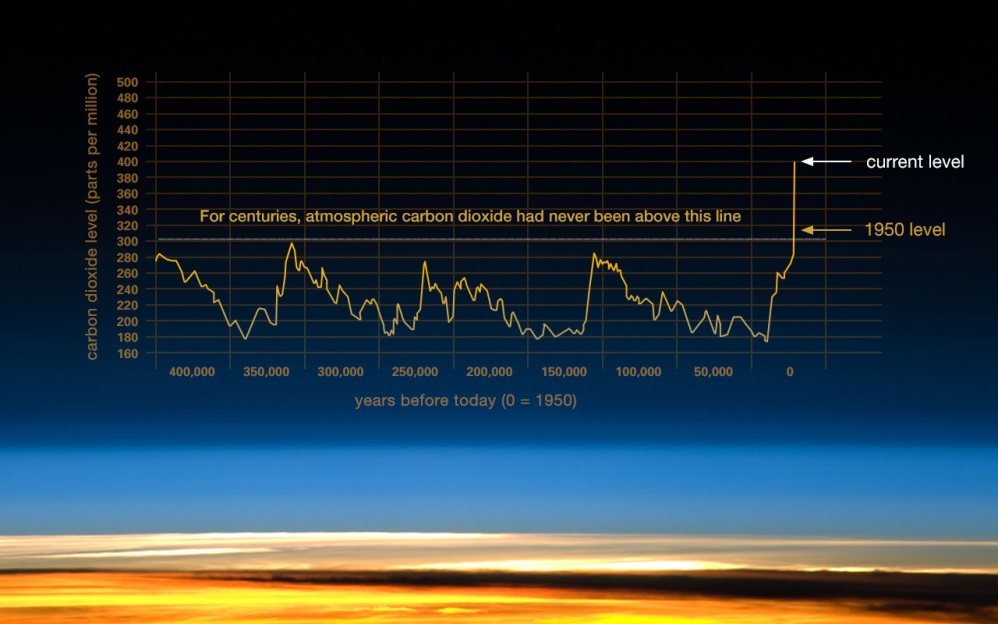



Causes And Greenhouse Effect



1




Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From
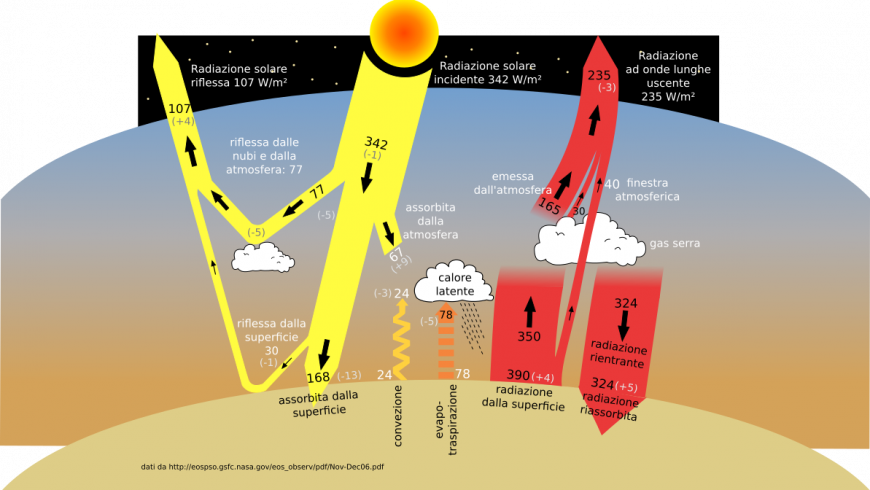



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions
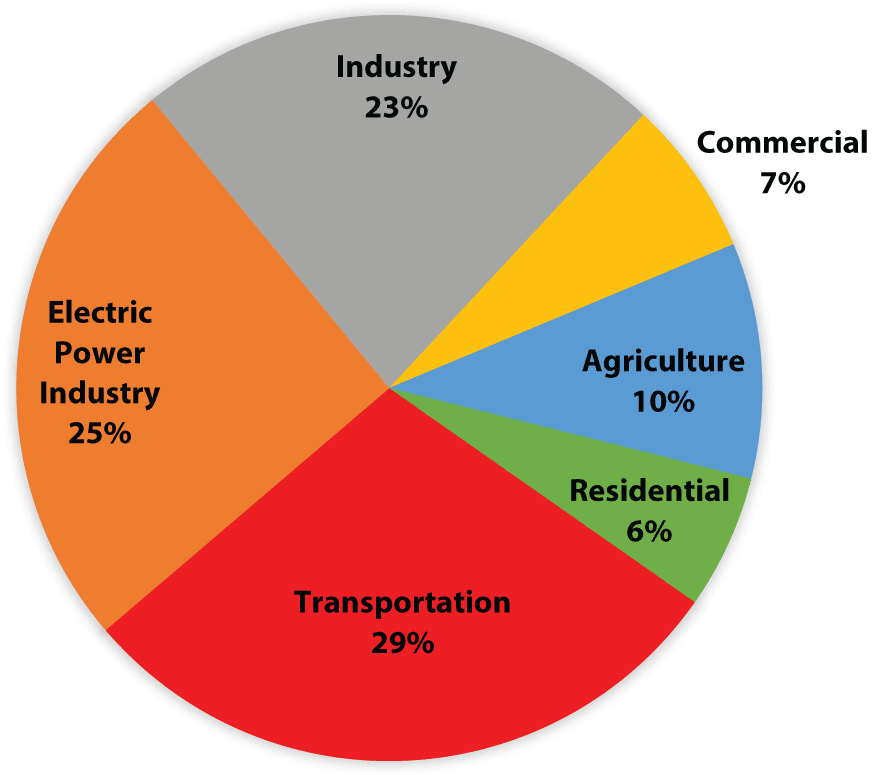



Agriculture And Greenhouse Gas Emissions G310 Mu Extension
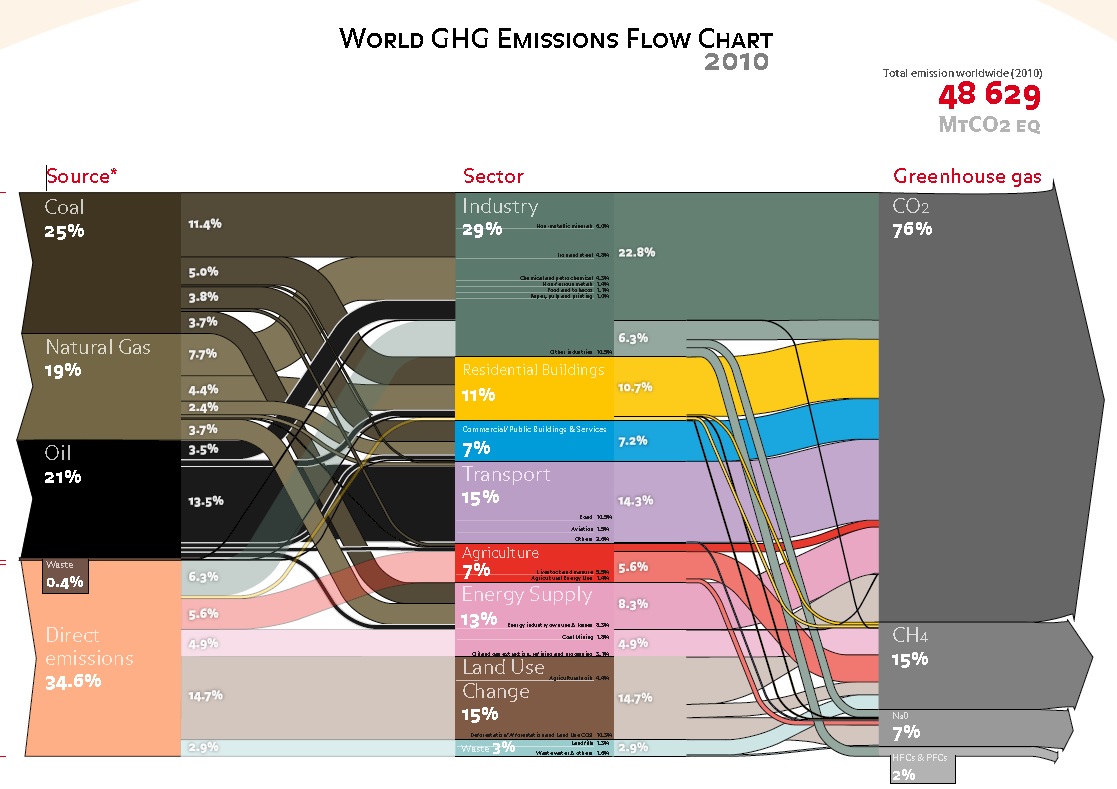



Greenhouse Gases Where They Really Come From Infographic
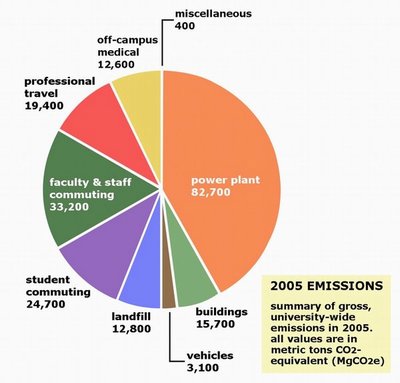



Uw Greenhouse Gases Down 10 Percent From 01 To 05 Inventory Finds Uw News
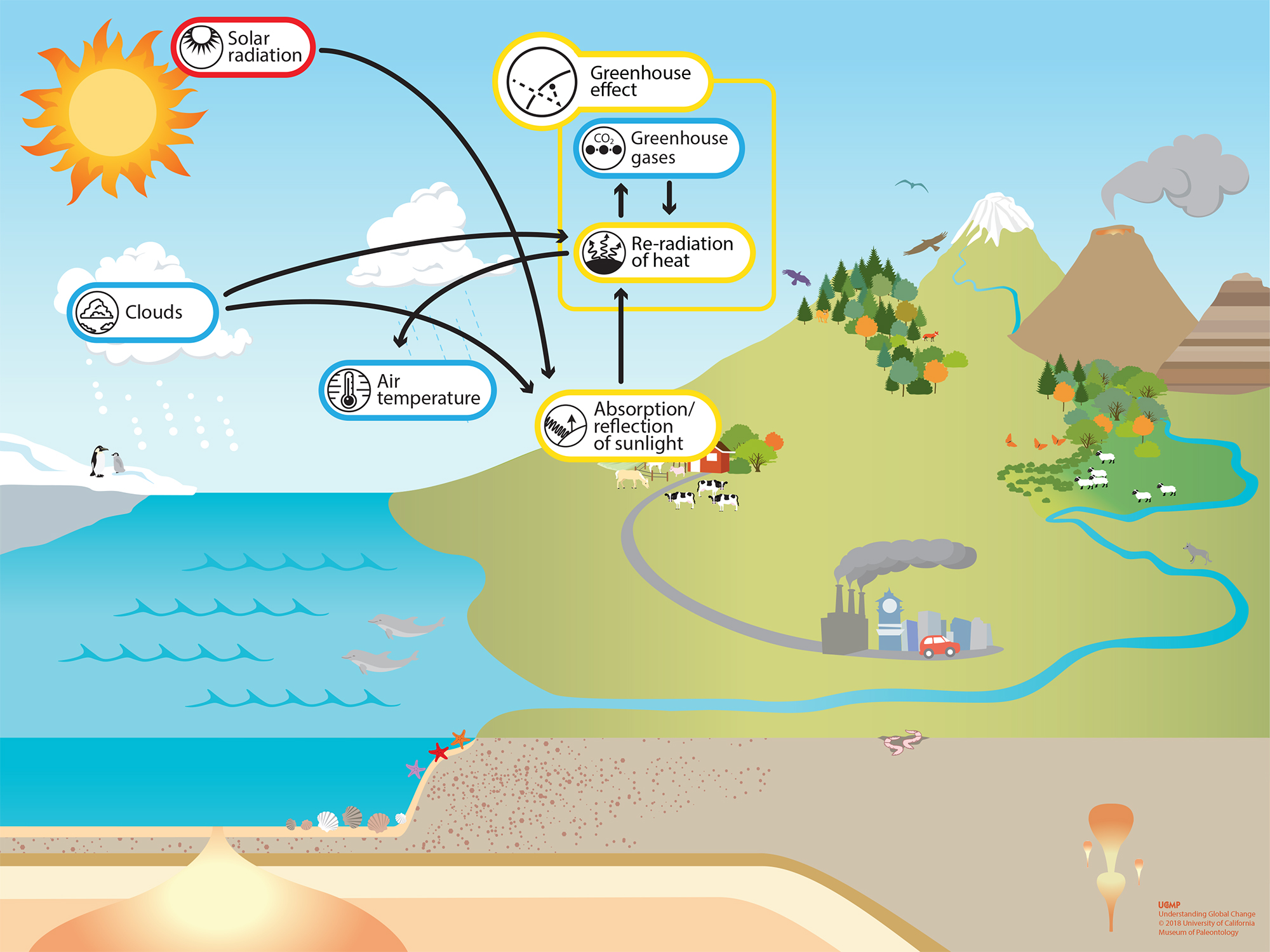



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
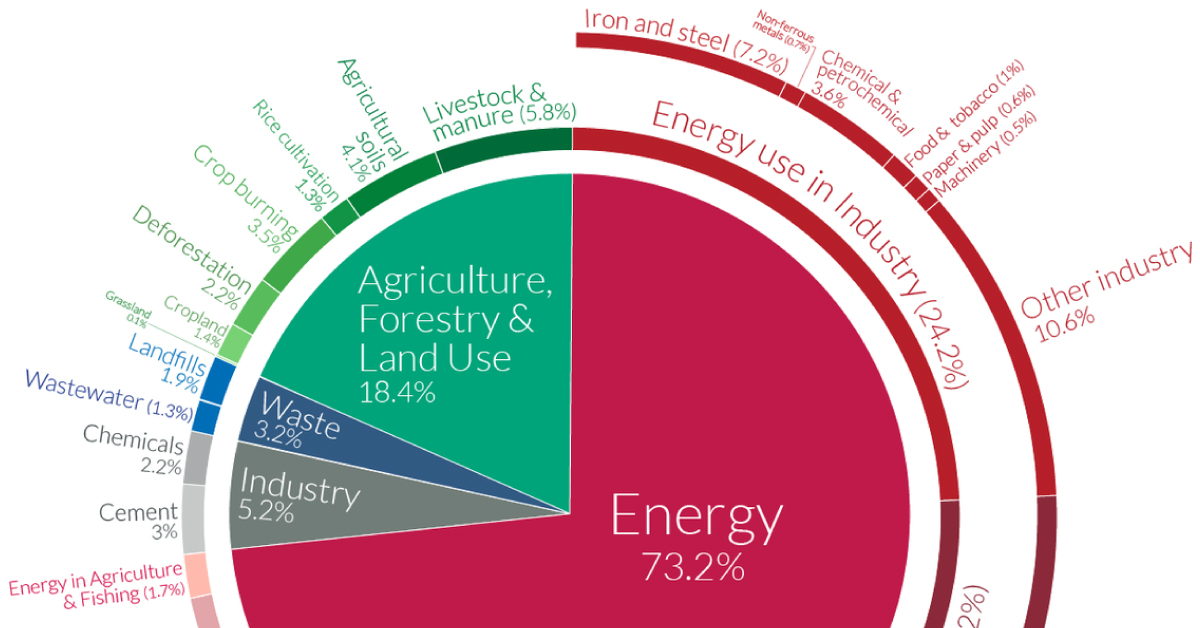



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Nh Department Of Environmental Services
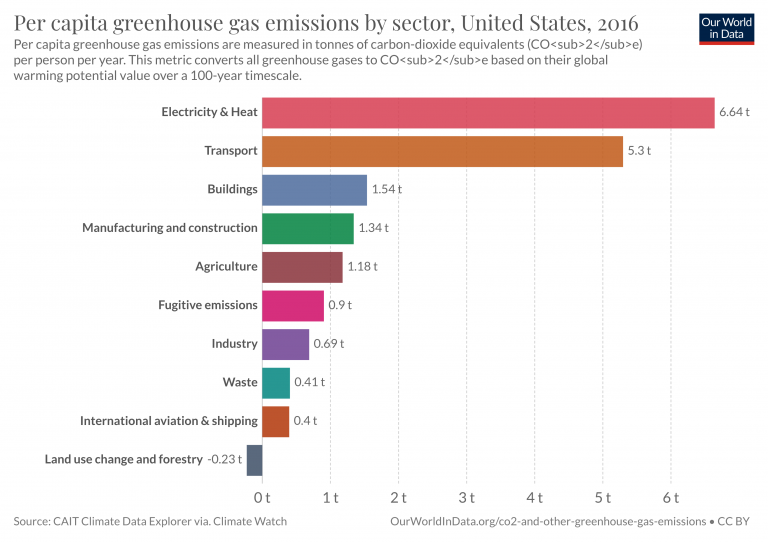



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/assets/4250823/ecofys-world-ghg-emissions-flowchart.png)



Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Vox




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
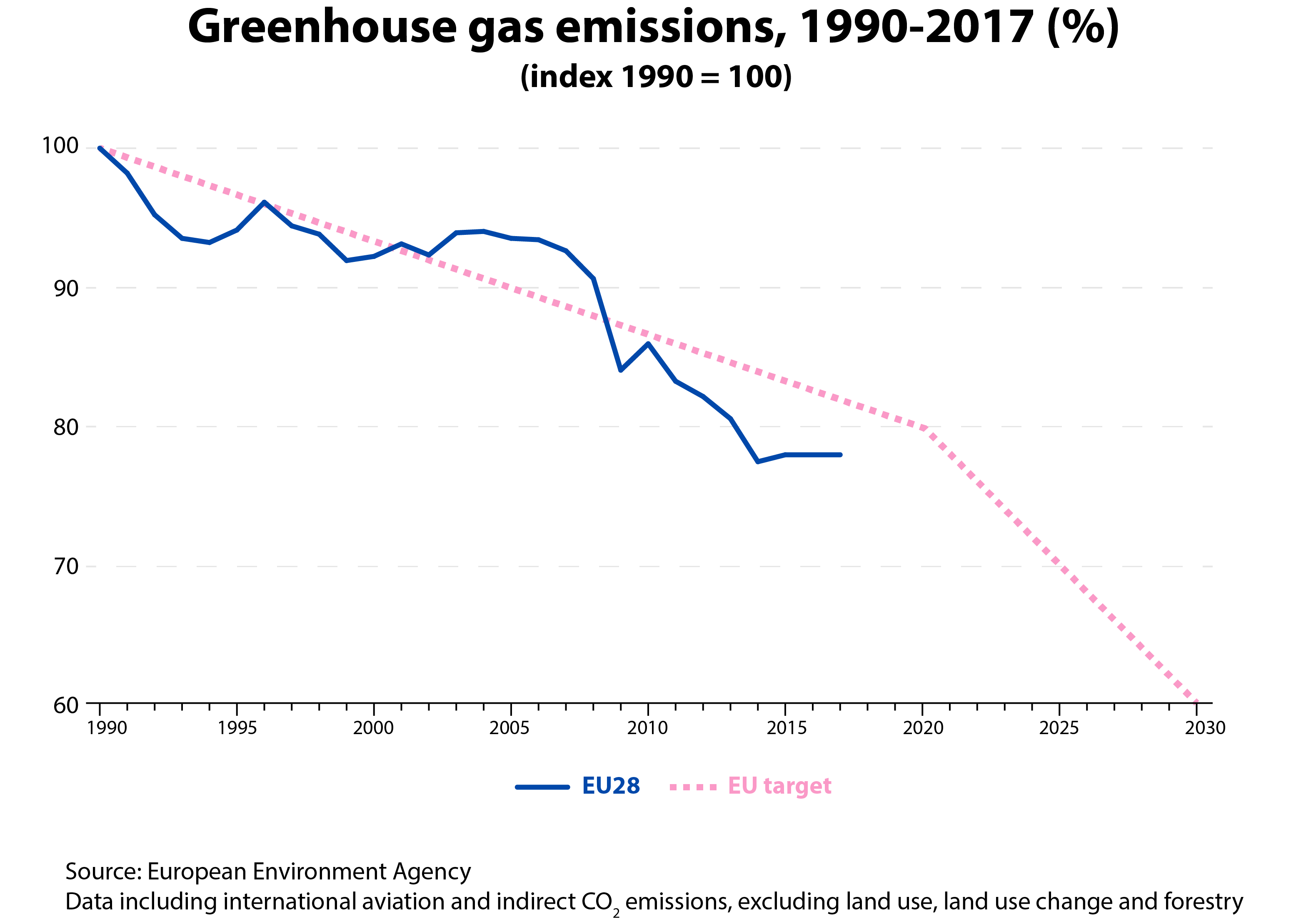



How Are Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases By The Eu Evolving
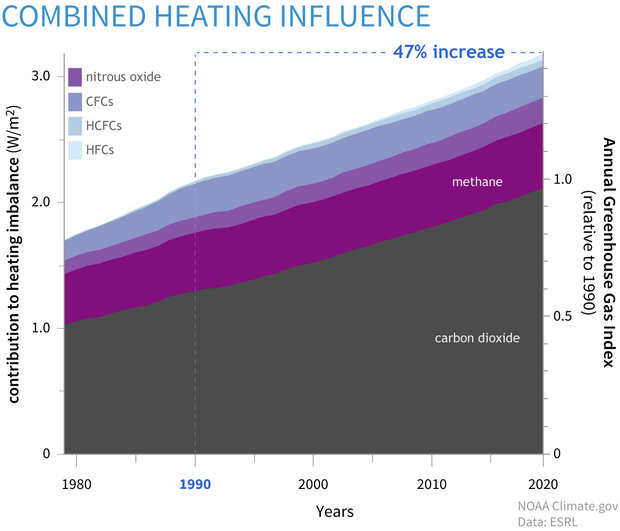



Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




California Plans To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions 40 By 30 Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
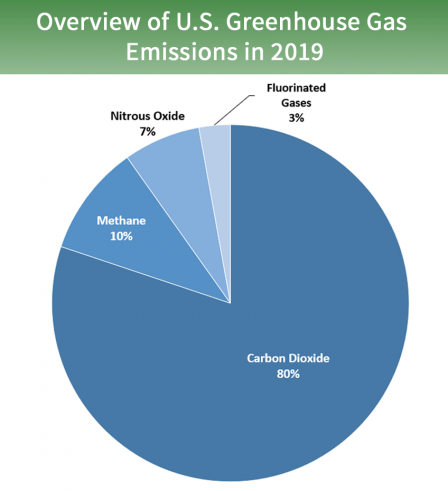



Why Are Greenhouse Gases A Problem




Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Vox




Chart Plastic S Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inside Climate News



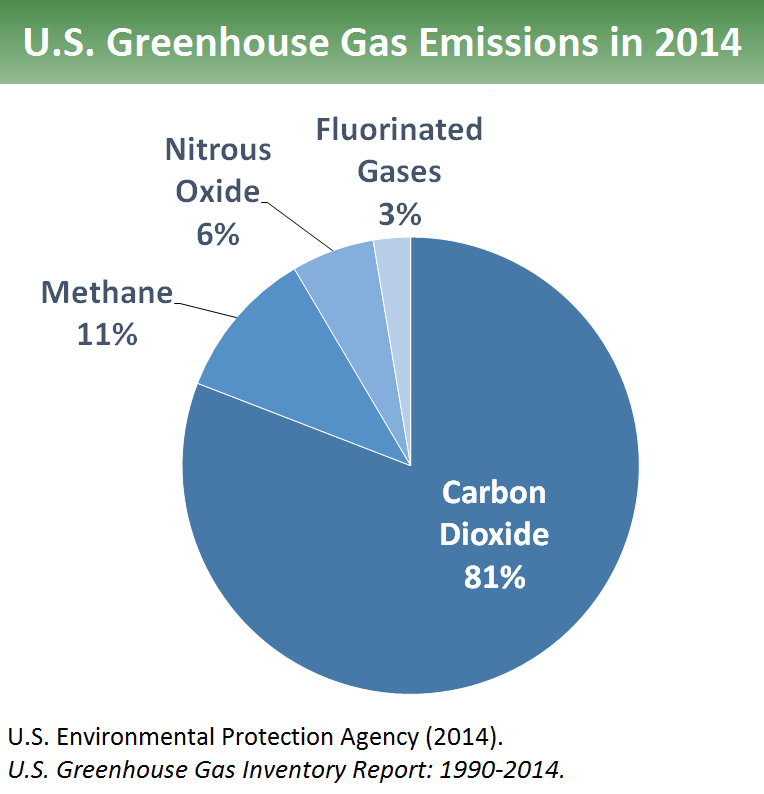
Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Eia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Overview




Indicator Greenhouse Gas Emissions Umweltbundesamt




Dnr Reports 3 Increase In Iowa Greenhouse Gas Emissions Iowa Environmental Focus




The Greenhouse Gases Airclim
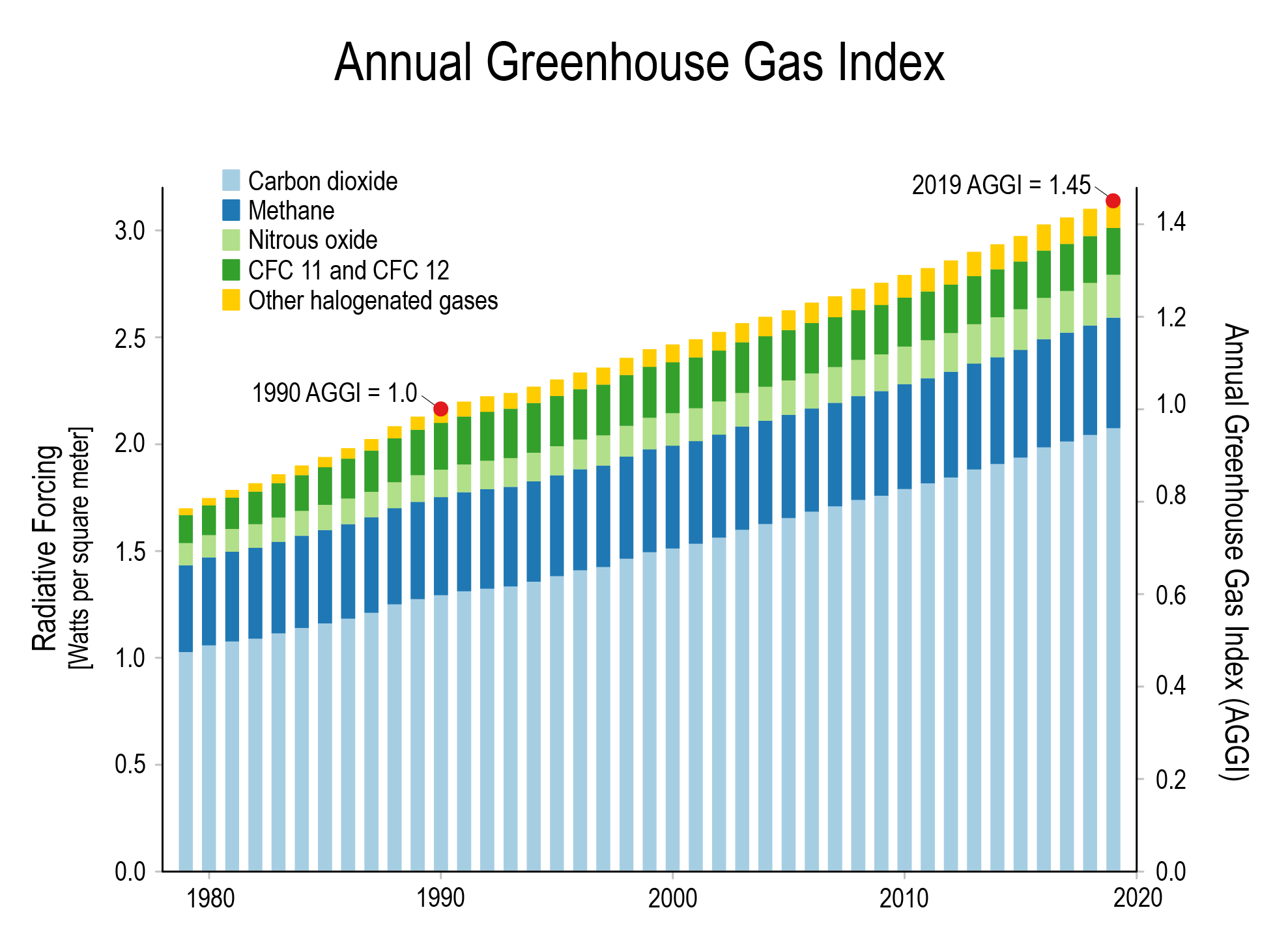



Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Global Gas Emissions Climate Energy And Society College Of Liberal Arts Auburn University




Reducing Greenhouse Gases Washington State Department Of Ecology




Airresources Greenhouse Gas Emission Chart Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng



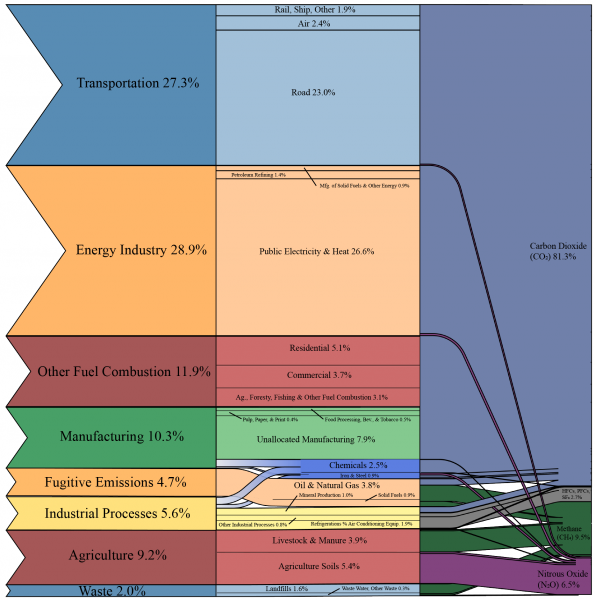
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Ghg Flow Chart Greenhouse Gases Ghg Emissions Greenhouse Gas Emissions
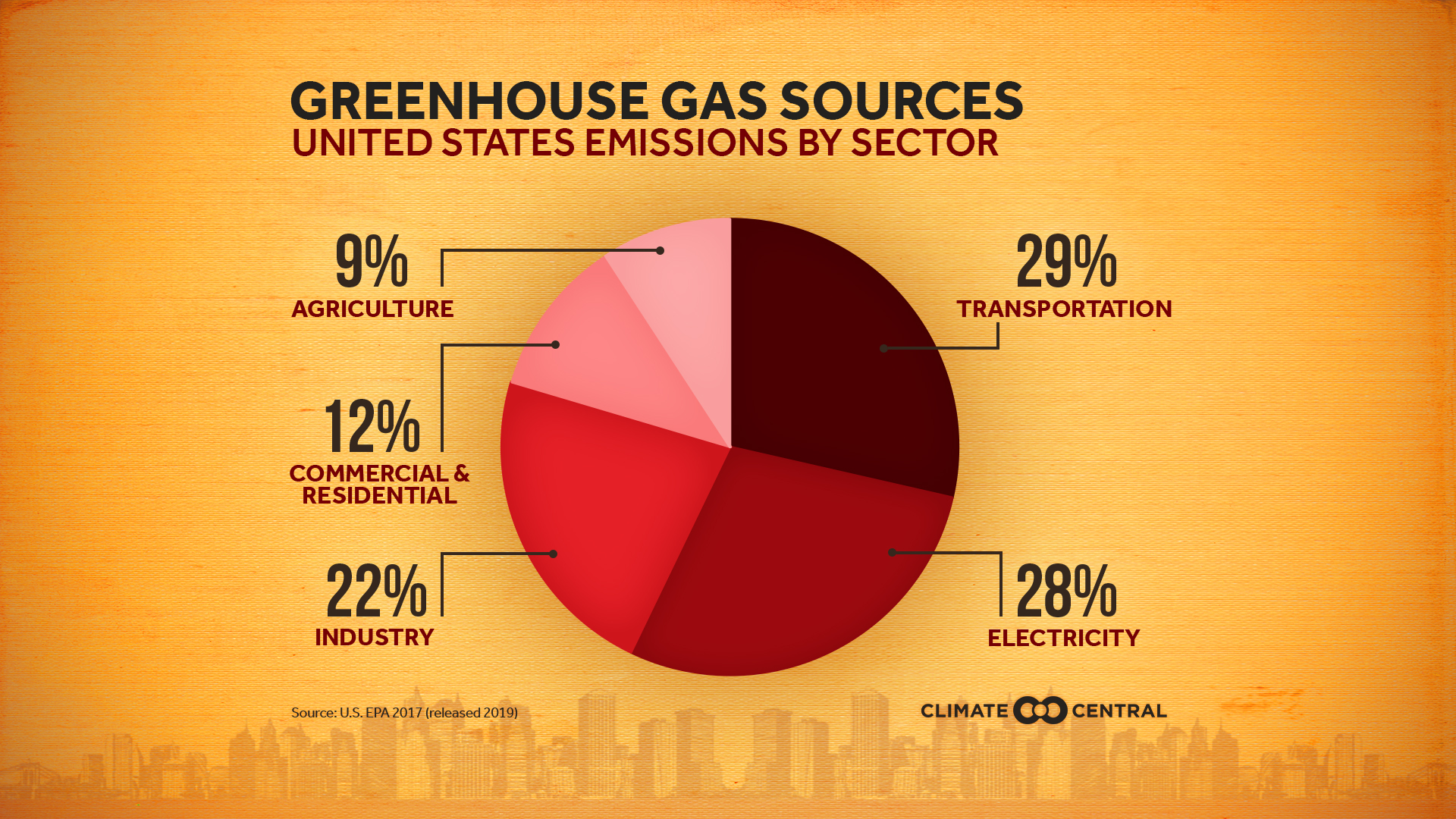



Emissions Sources Climate Central




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing How The Greenhouse Effect Works Global Warming Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image



The Greenhouse Effect



3
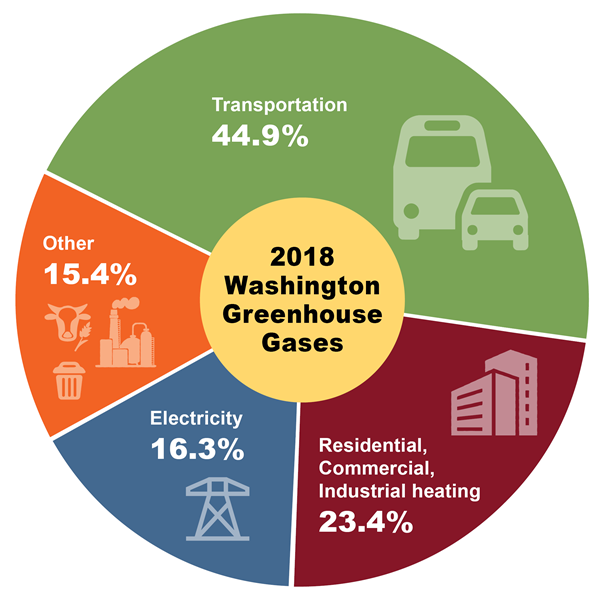



18 Data Washington State Department Of Ecology




Windsor S Greenhouse Gas Emissions




A Pie Chart Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
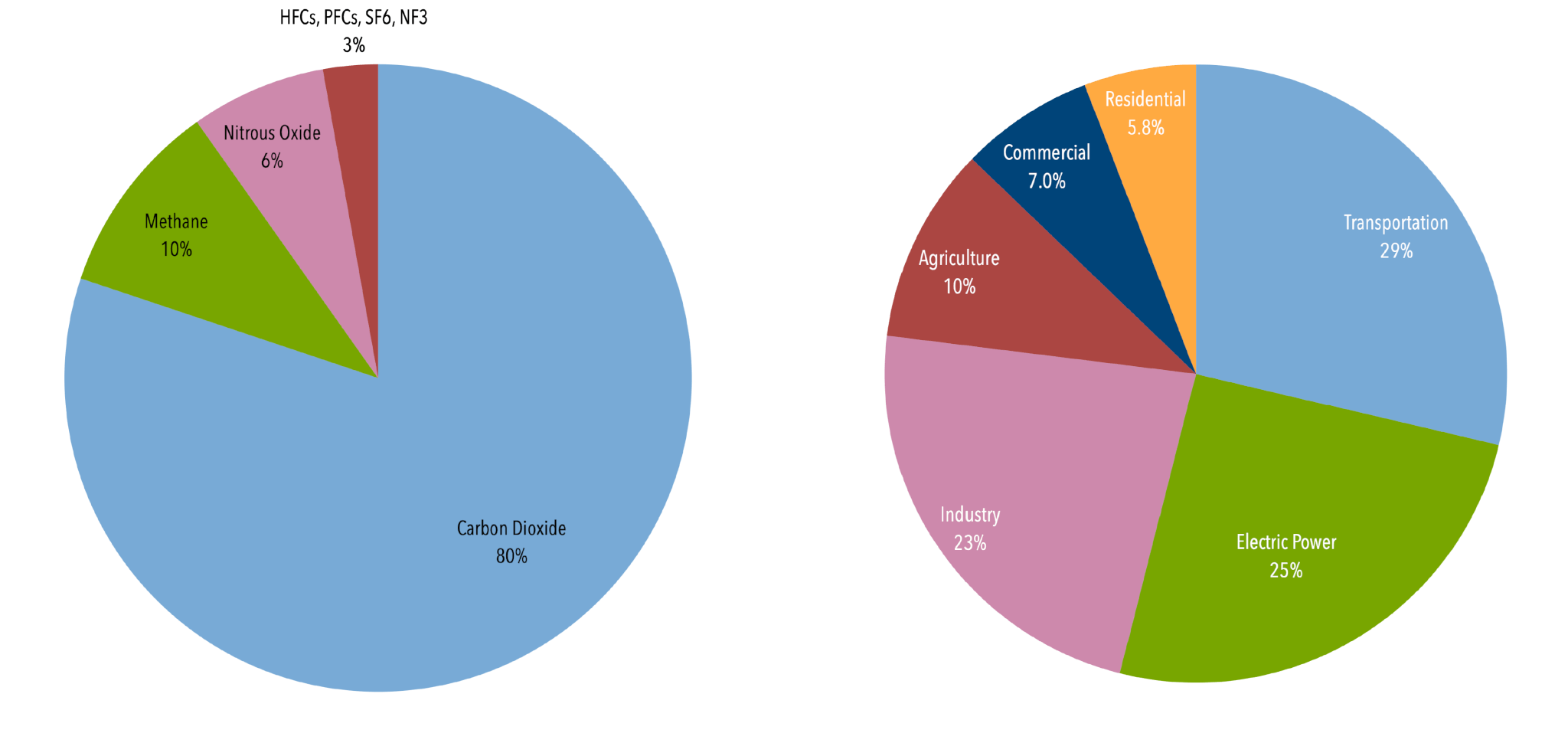



U S Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Ghg 101 Understanding Greenhouse Gases Canada S Oil Sands Innovation Alliance Cosia
コメント
コメントを投稿